Thalassemia is an inherited blood disease in which you have fewer red blood cells and less hemoglobin than normal. Hemoglobin is an essential protein that is present in your red blood cells. It performs the function of oxygen transport to various organs of the body. If the hemoglobin is low as compared to your need, your organs may lack oxygen. Thalassemia causes anemia- a condition in which your body lacks red blood cells, hence hemoglobin. If your child is diagnosed with thalassemia, you should visit the hematologist in Lahore.
For the formation of hemoglobin, various genes take part. In thalassemia, a defect occurs in the alpha or beta chain that forms hemoglobin. Sometimes you may only be the carrier of thalassemia when one of your parents passes it on to you. When both of your parents pass on the mutated genes of thalassemia to you, it shows up as thalassemia major- the symptomatic one.
Causes
Thalassemia is a genetic disorder- means you have it from birth. Your parents pass it on to you. Thalassemia that causes symptoms is known as thalassemia major. It occurs when both of your parents pass on the mutated genes to you. You can not acquire thalassemia from someone else like you catch flu or any other infection. When either one of your parents passes on their mutated genes to you, it may show up as thalassemia minor- when it does not show any symptoms.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of thalassemia may show up as;
Stunt growth in children
Brittle or wide bones
Fatigue
Weakness
Dark urine
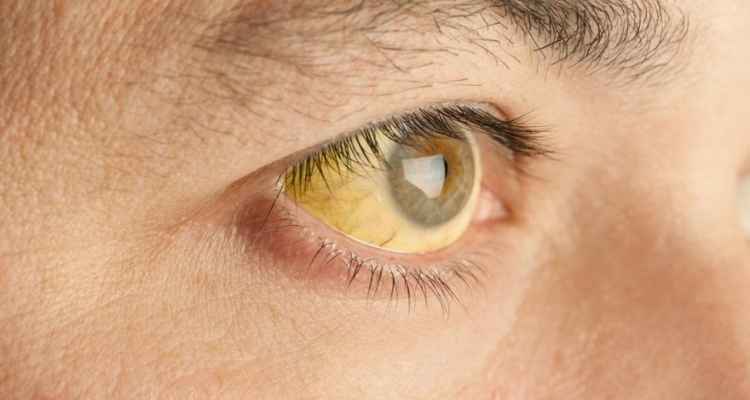
Pale or yellow skin
Heart problems
Poor appetite
Enlarged spleen- because the spleen is known as the graveyard of red blood cells. When your red blood cells die before their designated life that is around 120 days, the spleen becomes enlarged due to a high influx of red blood cells die.
In some people, symptoms of thalassemia can be observed at the time of birth. In some people, it may show up later. While in some people, it may not show any symptoms.
Home care for patients with thalassemia
If you have thalassemia, following home care tips may help.
Eat a healthy and balanced diet that helps in keeping your bones strong and gives you enough energy.
See your doctor for follow-up visits and especially if you have fever or breathlessness.
Wash your hands often.
Avoid staying with people who have an infection, especially respiratory tract infections.
Your doctor may prescribe you supplements like calcium and vitamin D that helps in keeping bones strong. You must take them on time.
Do not take iron pills.
Ask your healthcare provider before taking any medicine that your healthcare provider has not prescribed.
If you have mild thalassemia, you may feel fatigued but may not need treatment. But if it becomes severe, your organs may become deprived of oxygen. For its treatment, you might need;
Blood transfusion– it is a procedure in which blood is transfused into your body after someone donates it. How many transfusions you need in a month varies upon your condition. However, too much blood transfusion can lead to iron deposits around your heart lining. Your healthcare provider will prescribe medication to prevent that.
Chelation therapy– to prevent iron deposits around your organs due to repeated blood transfusions, your healthcare provider will prescribe chelation therapy that includes desferrioxamine.
Stem cell or bone marrow transplant– an infusion of stem cells from a matched donor can sometimes help cure thalassemia.
Supplementation– to prevent anemia, your healthcare provider will prescribe your folic acid or other supplementation.
Surgery– sometimes removing the spleen can help in the symptomatic treatment of thalassemia.
Complications
Thalassemia can cause various complications due to anemia, which can even lead to death. People with thalassemia may have the following complications;
Bones may become thin and brittle.
Iron overload due to repeated blood transfusion.
Your bones may have slowed growth because your bones do not grow normally.
Enlarged spleen due to increased damage to red blood cells.
Heart problems such as congestive heart failure and abnormal heart rhythm.
Conclusion
Thalassemia is a genetic disease that parents pass on to their children. If your child is diagnosed with it, you should visit the healthcare provider for follow-up visits. For that, you can visit a hematologist in Karachi.